Lateral loads
Lateral loads are live loads that are applied parallel to the ground; that is, they are horizontal forces acting on a structure. They are different to gravity loads for example which are vertical, downward forces.
The most common types are:
Wind load may not be a significant concern for small, massive, low-level buildings, but becomes more importance with height, the use of lighter materials and the use of shapes that may affect the flow of air, typically roof forms.
Significant seismic loads can be imposed on a structure during an earthquake. They are likely to be relatively instantaneous loads compared to wind loads. Buildings in areas of seismic activity need to be carefully designed to ensure they do not fail if an earthquake should occur.
Water pressure tends to exert a lateral load which increases linearly with depth and is proportional to the liquid density. Similarly, earth pressure (such as settlement) can be applied against below-ground structures such as basement walls, retaining walls, and so on.
Lateral loads such as wind load, water and earth pressure have the potential to become an uplift force (an upward pressure applied to a structure that has the potential to raise it relative to its surroundings). For more information, see Uplift force.
Structures should be designed carefully with likely lateral loads in mind. A structural element that is typically used to resist lateral loads is a shear wall. In simple terms, lateral forces could push over parallel structural panels of a building were it not for perpendicular shear walls keeping them upright. For more information see: Shear wall.
Similarly, bracing can be used to resist lateral loads. The beams and columns of a braced frame structure carry vertical loads, whilst the bracing carries the lateral loads. For more information, see Braced frame structure.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Bearing capacity.
- Bending moment.
- Biaxial bending.
- Braced frame.
- Dead loads.
- Floor loading.
- Force.
- Ground heave.
- Hurricane design considerations.
- Limit state design.
- Live loads.
- Loadbearing capacity.
- Moment.
- Point of contraflexure.
- Settlement of buildings.
- Shear force.
- Shear wall.
- Structural engineer.
- The design of temporary structures and wind adjacent to tall buildings.
- Torsion.
- Types of structural load.
- Uniformly Distributed Load.
- Uplift force.
- Vibrations.
- Wind load.
Featured articles and news
The first line of defence against rain, wind and snow.
Building Safety recap January, 2026
What we missed at the end of last year, and at the start of this...
National Apprenticeship Week 2026, 9-15 Feb
Shining a light on the positive impacts for businesses, their apprentices and the wider economy alike.
Applications and benefits of acoustic flooring
From commercial to retail.
From solid to sprung and ribbed to raised.
Strengthening industry collaboration in Hong Kong
Hong Kong Institute of Construction and The Chartered Institute of Building sign Memorandum of Understanding.
A detailed description from the experts at Cornish Lime.
IHBC planning for growth with corporate plan development
Grow with the Institute by volunteering and CP25 consultation.
Connecting ambition and action for designers and specifiers.
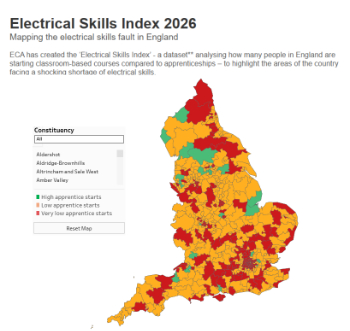
Electrical skills gap deepens as apprenticeship starts fall despite surging demand says ECA.
Built environment bodies deepen joint action on EDI
B.E.Inclusive initiative agree next phase of joint equity, diversity and inclusion (EDI) action plan.
Recognising culture as key to sustainable economic growth
Creative UK Provocation paper: Culture as Growth Infrastructure.
Futurebuild and UK Construction Week London Unite
Creating the UK’s Built Environment Super Event and over 25 other key partnerships.
Welsh and Scottish 2026 elections
Manifestos for the built environment for upcoming same May day elections.
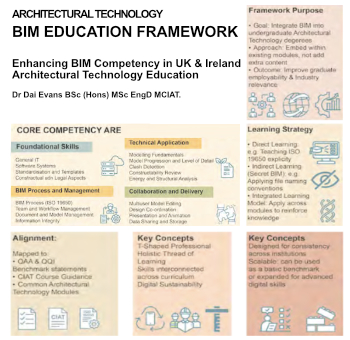
Advancing BIM education with a competency framework
“We don’t need people who can just draw in 3D. We need people who can think in data.”